Organs of the Immune System | Biotechnology
Throughout our body, many organs play an important role in the immune system. These organs
are referred to as the organs of the
Immune System or the lymphoid
organs.
Today, we will be getting answers to many basic
questions which come up with the topic. These are:
·
What are the organs of Immune
System ?
·
Why they are known as lymphoid
organs ?
·
What are the types of Organs of the Immune System ?
·
How lymphoid organs work in
Immunological system ?
·
In which way, is lymphatic system
associated with the Organs ?
·
How cells of Immune system are
different from the Lymphoid organs or Organs of the Immune System ?
So, let’s
just start the learning…
Our Immune
System is composed of various organs and vessel shaped structure like our much
known lymphatic system.
They all work together to defend or protect our body
against pathogens and viral infected cells.
Organs are positioned throughout our body and lymphoid organs play an important role
in producing, housing and in maturation
of lymphocytes.
The movement of lymph between tissues and blood
stream include the lymph, nodes and vessels are known as Lymphatic System.
The Lymphatic System produces antibodies and functions the immune processes or immune
response.
Types
of Lymphoid Organs
:
Here, we will highlight two main types of lymphoid organs. They are
1.
Primary
Lymphoid Organs
2.
Secondary
Lymphoid Organs
1. Primary
Lymphoid Organs :
Ø These
organs are also known as Central
Lymphocyte Organs.
Ø It
is the place of lymphocyte maturation.
Ø Stem
cells divide in primary lymphoid organs and become immunocompetent (ability of cells to evoke immune response).
Ø Largest
part of the lymphocyte development
occurs in primary lymphoid organs.
Ø The
major primary lymphoid organs are:
a.
Thymus
b.
Bone
marrow
a.
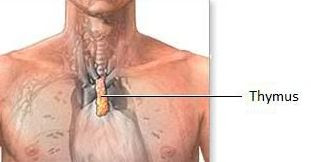
Thymus
:
The most specialized
organ of the immune system is thymus.
It is placed in front of heart and behind
the sternum.
T cells develop from hematopoietic cells (stem
cells) and mature in thymus, so the cells are referred to as ‘T’.
The tolerancy of T cells to the body cells takes
place in thymus only.
Thymus, being the largest immune organ is most active in newborn and during pre
adolescent period.
Thymus slows down during teen period, but the
production of lymphocytes is carried out throughout adult life.
b.
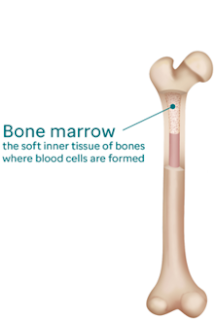
Bone
marrow :
Bone
marrow is a tissue present in hollow bones and mainly makes new blood cells.
Bone marrow is mainly categorized into two types : Red marrow and Yellow marrow.
Red
marrow is mainly composed of myeloid tissue. Red blood cells, majority of White blood cells and platelets are
produced in red marrow only.
Red marrow is present nearly in every bone in a
child.
In adults,
Red marrow is present in skull, ribs,
sternum, vertebrae, a part of pelvic girdle and proximal heads of humerus and
femur.
Yellow
marrow is mainly made up of fat cells. Most of the blood
cells and capillaries are there in Yellow marrow.
Yellow marrow is present in adults only and produces
no blood.
Yellow marrow is majorly found in medullary cavity of long bones.
The word ‘B’ in B cells is taken from bone marrow,
because it is the site of B cell development and maturation.
2. Secondary
Lymphoid Organs :
Ø They
initiate Adaptive immune response.
Ø These
organs provide space or site for interaction
of lymphocytes with antigen.
Ø The
lymphocyte – antigen interaction then multiplies to become effector cells.
Ø The
secondary lymphoid organs increase in size with age.
Ø These
lymphoid organs comprises of :
a.
Spleen
b.
Lymph
nodes
c.
Tonsils
and Adenoids
d.
Peyer’s
patches
e.
Appendix
a.
Spleen
:
This organ i.e. spleen
is a part of the lymphatic system and in humans; it is on the left side of the body, under the heart.
The spleen fights against infections, and make sure
to keep the body cells healthy.
The spleen clear
up old blood cells from the blood, and restores iron and amino acids from the
old blood cells.
The spleen carries a stock of extra blood, if needed
by the body.
It works in co-ordination with the circulatory
system.
The spleen acts as a reservoir which carries over half
the body’s monocytes.
The immunity mechanism works as,
Monocytes
----à Injured tissue --à
Dendritic cells and Macrophages --à
Tissue healing
b.
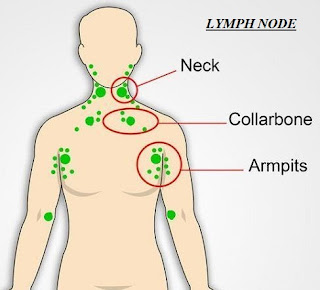
Lymph
nodes :
Lymph
node
is an organ comprising of many types of cell and is an integral part of the
lymphatic system.
Lymph nodes are found throughout the body and
contain white blood cells.
They are responsible for the proper working of
Immune system.
Lymph Nodes are mostly found in neck, underarm and groin region.
The lymph nodes swell up in the area of infected
body part which keeps away the spreading of infection.
They refrain or reduce the pathogens to go through
general body circulation and thus preventing the reach of pathogens to other
parts of the body.
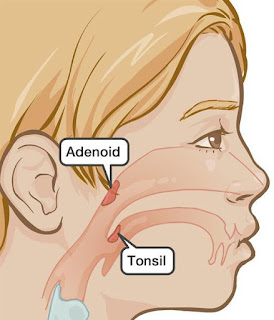
c.
Tonsils
and Adenoids :
Tonsils
are referred to as the lymphoid tissue
areas present on the either side of the throat.
Infection of tonsils is called tonsillitis.
The word ‘tonsil’ is mostly referred to the palantine tonsils that are seen in the
back of throat.
Tonsils’ are being a part of immune system, helps to
protect against infection.
They basically fight
off pharyngeal and upper respiratory tract infection.
Adenoids
are also referred to as pharyngeal tonsils or nasopharyngeal tonsils which are present at
the very back of the nose.
They are present in that part of nose which joins
the mouth.
In children, sometimes they make a soft bump in the top and back section of
the nasal air passage.
Removal of adenoids with surgery is called Adenoidectomy.
d.
Peyer’s
patches :
Peyer’s
patches are commonly referred as “tonsils of intestine”.
These patches are found in the wall of ilium region of small intestine where they capture and
destroy bacteria present in the intestine.
Peyer’s patches are round and oval in shape which
can be seen with naked eye.
They play a defined role in evoking immunologic
response, as they contain both B cells and T cells.
These cells are similar to those found in peripheral lymph node.
Peyer’s patches work in the following manner :
Take
up foreign material or bacteria ----> submucosal macrophages----à
macrophage processing ----à
T cells and B cells.
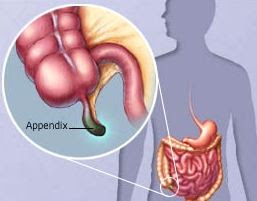
e.
Appendix
:
The ‘appendix’
is a pouch present at the beginning of large intestine.
It is a blind
ended tube shape structure which helps immune system by supporting the growth of beneficial gut flora.
Appendix acts as a ‘safe house’ for
bacteria which help in digestion.
Appendicitis
is the swelling of appendix and one of the main causes of abdominal pain
worldwide.
So, the above discussion gives us an insight about the
various organs which are associated with the Immune System.
To know more about our immune system, its types and the cells involved in the immunogenic
process, you can go through my Previous blogs to get more understanding on the Immune System basics and previously explained topics
Much
more to share, stay connected!!!
Keep
smiling n boost up your immune system.
Happy
Bio Technology Learning!!!