Cells
of Immune System
BioTechnology,
Immune System
·
Cells of Immune system?
·
Types of cells of Immune system? How
these cells provide immunity in our body?
You must have above question in your mind right now.
In this post we will cover these questions and discuss about the various cells
involved in the immune system
machinery.
Cells of Immune system are already well explained in
my previous post on Innate or Natural Immunity,
please go through it for clear cut picture on Cells of Immune system.
In this post I will explain cells of Immune system
individually.
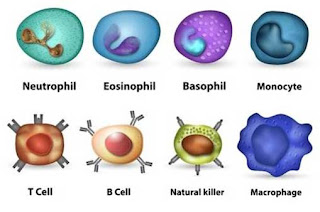
Types
of Immune cells:
1.
Lymphoid
Cells
2.
Mononuclear
Phagocytes
3.
Granulocytic
Cells
1.
Lymphoid
Cells
:
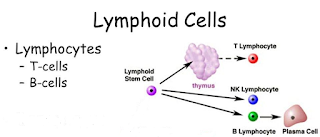
A network of thin blood vessels
branch into the tissues throughout our body known as lymphatic system.
This system transports infection fighting cells called lymphocytes.
Lymphoid
Cells are further divided into three types of cells-
·
B
Lymphocytes
·
T
Lymphocytes
·
Natural
Killer Cells
All readers can refer my post on Immune System Basic Concepts for clear information on the above mentioned cells.
Let’s proceed with T cells and B cells first,
1.1.
B
Lymphocytes:
B cells are a type of white blood cells which produce antibodies.
These cells have a protein on their outer surface known as B cell receptor and play an important role in adaptive immune response.
The main functions of B cells are:
·
They
produce antibodies against antigens
·
They
perform the role of antigen presenting cells(APC’s)
·
Developing
into memory B cells after activation by antigen presentation
They derive their name from their maturation place.
These cells mature into B lymphocytes
in bone marrow and so called as B lymphocytes.
1.2.
T
Lymphocytes :
It is a type of lymphocyte which plays an important
role in immune system by combating the virus
infected cells, foreign cells and cancer cells.
These cells mature
in thymus, so they are known as T cells.
Receptors present on their cell surface for proper
working of these cells are known as T
cell receptors and plays a major role in providing immune response.
T cells are sub categorized into the following types/
Types of T cells -
1)
Cytotoxic
T cells (Tc cells)
2)
Regulatory
T cells or Suppressor T cells
3)
Natural
killer cells (NKT cells)
4)
Helper
T cells (Th cells)
5)
γδ T
cells
These cells ‘tackle’
the infectious agent and make immune system ‘remember’
the event.
T helper cells produce
cytokines which direct the Immune System.
Cytokines in turn signal other immune cells about the presence of an infectious
agent.
Cytotoxic
T cells come to the rescue and produce toxic granules leading to the death of infectious agent.
Characteristics
of types of T cells:
Ø Cytotoxic T cells
and Natural killer cells works in
accordance in lysis of viral infected cells,
tumor cells and allografts (a unit of organ transplantation).
Ø Helper T cells
release cytokines and growth factors
for regulation of other immune cells.
Ø Gamma/ delta T cells
work in process of immunoregulation and
cytotoxicity.
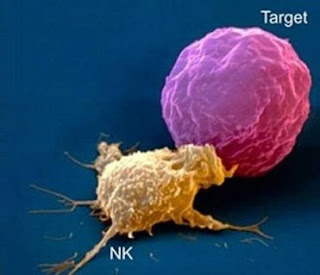
1.3.
Natural
killer cells :
A subtle information about these cells were
explained in
Natural
killer cells provide a rapid response to virus infected cells and bacterial cells and
more importantly in tumor formation.
In Immunological sciences, there is a saying, “Natural killer cells are unique”.
The reasons
behind this statement is,
a)
Ability
to recognize stressed cells in absence of antibodies and major
histocompatibility complex.
b)
Faster
immune response.
Natural
killer cells Function:
Natural killer cells have two
types of receptor on their cell surface i.e.
§ Activating Receptors
§ Inhibitory Receptors
During Natural killer cells activation, it kills the
cell depending on the type of receptor
switched on.
Mechanism
of Action:
a.
Cytoplasm
of NK cells contain protein and enzymes called Granzymes.
b.
These
enzymes are released close to the cells, which has triggered their action.
c.
A
protein perforin forms pore in the cell membrane of target cells, allowing the
entry of enzymes through, leading to the killing of target cells.
2.
Mononuclear
Phagocytes:
The briefing of phagocytic process is already provided
in the
Previously Mononuclear Phagocyte System was known as Reticuloendothelial System.
These phagocytes work
in a systemic order to kill pathogen.
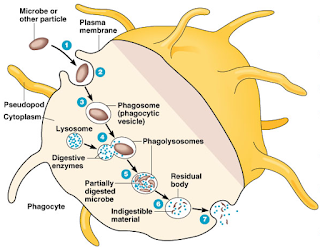
Working behavior:
·
The
pathogen gets attached or adhere to the plasma membrane of phagocyte preferably by chemotaxis.
·
The
pathogen is ingested by phagocyte.
·
A
phagosome is formed around the
pathogen.
·
This
phagosome gets fused with the lysosome of the phagocyte to form phagolysosome.
·
The
digestive enzymes produced kills the pathogen.
·
A
residual body is formed for the indigestible material of pathogen.
·
This
residual body is discharged off from the phagocytes.
The process of killing of pathogen or phagocytosis
is the main centre of study for phagocytes.
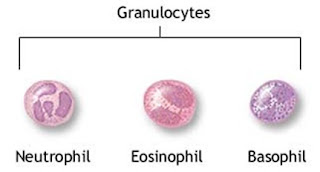
3.
Granulocytic
Cells:
These are the lymphocytes or white blood cells which
have granules in their cytoplasm.
Their nucleus
comprises of three segments and they
are released from bone marrow.
These cells operate by phagocytosis as well as by
other means also.
Types
of Granulocytic Cells:
Based on their appearance, these cells are
categorized into the following types;
3.1.
Neutrophil
Granulocytes
3.2.
Eosinophil
Granulocytes
3.3.
Basophil
Granulocytes
3.1.
Neutrophils:
They are the most common type of
white blood cells and are known as neutrophil granulocytes.
These cells play an important role
in immune system and have a very short life span.
Action Mechanism:
§ Neutrophil granulocytes migrate
from blood vessels into matrix.
§ On reaching inside matrix, they
start secreting enzymes and peptides which dissolve intercellular connections.
§ Dissolution of these connections
improves the neutrophil mobility.
§ Being mobile, neutrophils engulf
bacteria and kill them through phagocytosis.
3.2.
Eosinophils:
 |
| Eosinophils |
These are the granulocytes which
combat with parasites and fights infection.
On activation, they release huge
amount of proteins like heparin from
their granules.
Points to Remember –
·
These cells comprise of bilobed nucleus and are defensive
against large multicellular parasites like worms
and flukes.
·
The most characteristic feature of
eosinophils is that they increase in
number during an infection.
·
They are also known as Acidophils.
3.3.
Basophils
:
They
are referred to as Rare Granulocytes.
Points to Remember –
·
Being a circulating granulocyte,
basophils travel from blood into a tissue when needed.
·
They
have protein receptors on their cell membrane which binds with IgE, an
immunoglobin associated with allergy and macroparasite defence processes.
·
They are found unusually high in number during ectoparasitic infection i.e. by ticks.
·
They carry histamine and heparin for their immunogenic action on pathogens.
·
Mast
cells and dendritic cells are also a type of immune cells
and work in the following way.
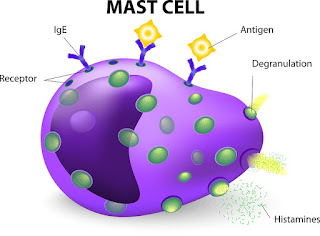
a)
Mast
Cells:
A mast cell is a white blood cell which works in tissues.
Points to Remember –
·
It is produced in bone marrow, and matures in tissues, to defend against
parasites.
·
Mast cells have granules which contain histamine and heparin.
·
They play a protective role in healing
wounds and defence against pathogens.
·
They are a major reason of allergy and anaphylaxis.
·
The
mast cell is very similar in appearance and function to the basophil, however, they are not the same.
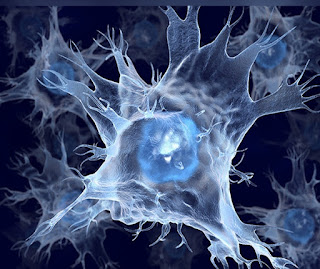
b.
Dendritic
Cells:
Dendritic
Cells are known as immune helper cells.
These cells serve three functions mainly,
·
Phagocytosis
·
Antigen presentation
·
Cytokine production.
Phagocytosis
is the process of uptake of microbes, their digestion and destruction.
Microbial fragments that remain after digestion act
as antigens.
This process is called antigen presentation and activates T
lymphocytes.
They make a specific immune response against the
antigen.
Other microbial products activate these cells and leads
to the production of pro-inflammatory
cytokines.
So, the topic “Cells
of immune system” comes to an end here, hoping to clarify the doubts of all
the readers.
Hope this post on ‘Cells of Immune System’ helped
you to understand the topic clearly.
You can follow my Facebook page @ FB/DeepaliTalk and
visit Blogs @ Learn BioTechnology with DeepaliTalk for
other posts on Immune System in BioTechnology.
Happy
Learning and Good Luck !!!